Currently available treatments and most of the competitor trials appear to be focused on reducing brain plaque buildup. I asked Perplexity why these treatments were considered controversial, and why Actinogen could improve the situation.
Discussion of the amyloid-beta treatment controversies
Aducanumab (Aduhelm) is a monoclonal antibody targeting amyloid-beta (Aβ) plaques in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), controversially approved by the FDA in 2021 under accelerated approval pathways. Here’s an analysis of its trajectory and Actinogen Medical’s potential role:
Aducanumab: Current Status
What Works
13. Amyloid Plaque Reduction
• Demonstrated 59%-71% amyloid plaque clearance on PET scans in phase 3 trials (EMERGE/ENGAGE), with dose-dependent effects.
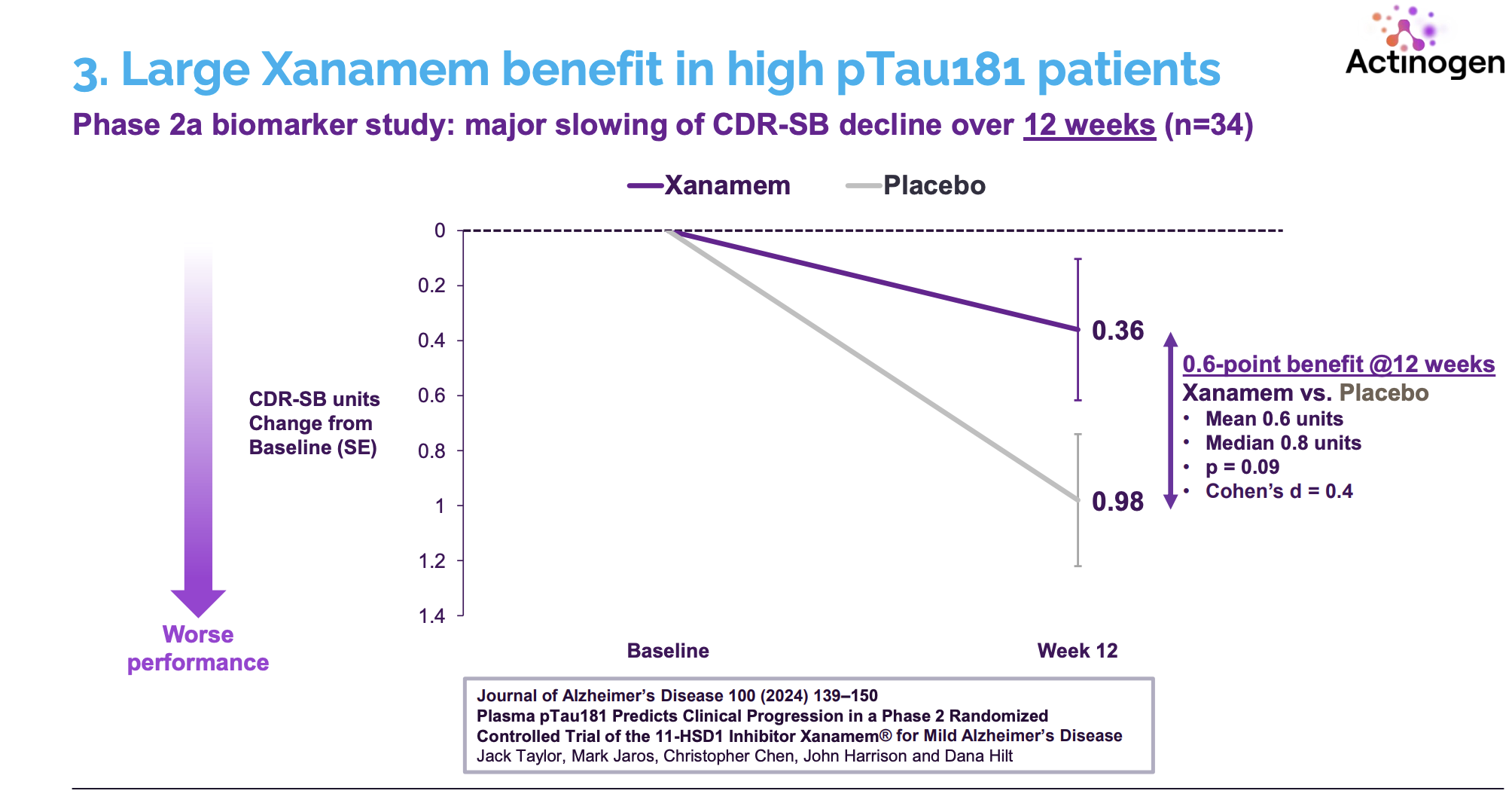
• Biomarker data showed reductions in plasma p-tau181, a downstream tau pathology marker.
14. Regulatory Precedent
• First amyloid-targeting drug approved since 2003, paving the way for newer anti-amyloid therapies like lecanemab and donanemab.
15. Subgroup Benefits
• In EMERGE, high-dose aducanumab showed a 22% relative reduction in cognitive decline (CDR-SB score) over 18 months vs. placebo.
Challenges
Issue Impact
Divergent Trial Results EMERGE (positive) vs. ENGAGE (neutral) raised validity concerns; post-hoc analyses deemed statistically fragile.
Safety Risks 35%-41% incidence of amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA-E/ARIA-H).
Cost & Access Priced at $56,000/year, with Medicare restricting coverage to clinical trials due to uncertain benefit.
Clinical Relevance Amyloid reduction ≠ cognitive improvement: CDR-SB difference of 0.39 points (vs. ~1.5-2.0 MCID).
Actinogen’s Position
Actinogen’s emestedastat (Xanamem) represents a paradigm shift from amyloid-centric approaches:
16. Mechanistic Advantage
• Targets brain cortisol via 11β-HSD1 inhibition, addressing neuroinflammation and synaptic dysfunction linked to Aβ/tau pathology.
• Phase 2 trials showed cognitive improvements in AD patients without amyloid-related safety signals.
17. Strategic Differentiation
• Oral administration vs. aducanumab’s IV infusions.
• Targets broader neurological conditions (e.g., depression, Fragile X) beyond AD.
18. Clinical Progress
• XanaMIA phase 2b/3 trial (n=220) uses pTau181 biomarker stratification, with interim results expected Q4 2025.
Key Debates
• Amyloid Hypothesis Validity: Aducanumab’s approval reignited skepticism about Aβ’s causal role in AD.
• Regulatory Trust: FDA’s accelerated approval faced criticism for prioritizing biomarkers over clinical outcomes.
• Market Dynamics: Lecanemab/donanemab now dominate amyloid-targeting pipelines, while Xanamem offers a cortisol-focused alternative.
Conclusion
Aducanumab’s legacy lies in accelerating AD drug development despite its commercial and scientific setbacks. Actinogen aims to supersede it by addressing cortisol dysregulation—a mechanism orthogonal to amyloid—with a safer oral therapy. While amyloid remains a therapeutic pillar, the field increasingly recognizes multifactorial approaches as essential for meaningful disease modification.