I’m a bit late in posting this feedback on the PNC meeting that I attended last week; it’s been a busy time and I’ve not had time to delve into the details until now. I’ve written this more as a way of capturing my learnings over the last week, but I thought to post it here for anyone else that might be interested. I might change this straw as I look more into Credit Corp (I’ve not seen their presentation yet).
General Information
PNC are a debt collection company founded in 2009 by Keith and they went public in 2014. The board and management own 21% of company.
They buy ‘purchased debt portfolios “PDPs”, from the major banks and some second tier (unstated) companies. PDPs are a collection of unpaid debts. The average customer they acquire through the PDP acquisitions owes on average $11k per product. The banks aren’t expert at recovering small amounts like this so they sell it to companies like Pioneer to free up that cash to put it back into their lending operations.
Keith said that their focus when it comes to debt acquisition is high quality credit products with consumers that have a reasonable prospect of getting ahead of their repayments. They operate in Australia only.
Keith said and it’s generally accepted that banks like to sell their debt portfolios to companies like PNC as they buy the debt as opposed to acting as an agent. This puts a requirement on PNC to adhere higher standards to maintain positive relationships with banks and regulators. This is ultimately better for the banks that have a reputation to protect too, and are subject to third party reputational risk depending on how companies like PNC operate.
The banks generally sell their accounts at 180 days past due. Pioneer get offered to buy a big basket of accounts (e.g., 1k at a time). The PNC analysts would then set about working out what the customer propensity to pay the total value is and work out a safe bid price to offer the bank. If successful, they then sign an agreement with the bank to buy the debt. From that point in time, the consumer is their customer and PNC send them a friendly ‘welcome to pioneer letter’ (as Keith put it) and pioneer work with them to recover the funds.
Keith has said (paraphrasing) that when they assess the value of the debt they’re buying, they start by looking at its ‘origination.’ I.e., what were the lending practices and standards that give rise and are wrapped around the debt. Then they take the most negative outlook they can find from any of the economic forecasters and feed this into their modelling. They’ve assumed significantly higher unemployment and they’ve assumed that people will pay less for a longer period of time. This is then reviewed by their investment committee. If the vote is not unanimous then they won’t proceed to buy the debt. Some of the executives have a significant proportion of their wealth in the decisions so they take great care to get it right.
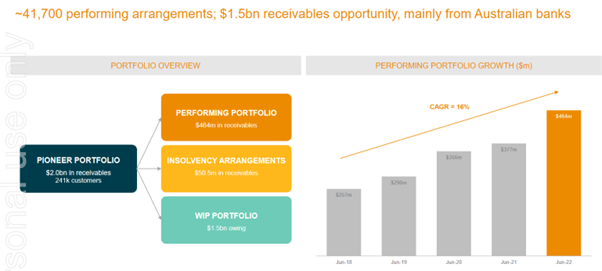
PNC need a healthy pipeline of debt or PDPs to grow their Work in Progress (WIP) portfolio, which can then be converted into paying customers, or their ‘Performing Portfolio’. Without an increase in the volume of their PDP acquisitions, they will not be able to increase their WIP portfolio and in time this will reduce their revenue.
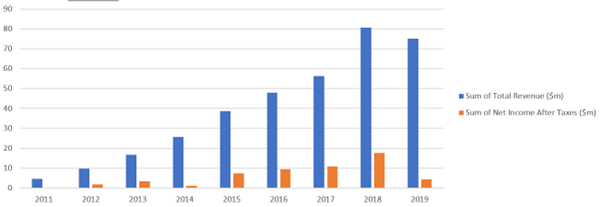
Since going public (2014) They’ve steadily increased revenue and NPAT until 2019. Their 1 April 2019 had NPAT guidance of $20m but due to changing accounting practices, this was subsequently reduced to 4k (see below)
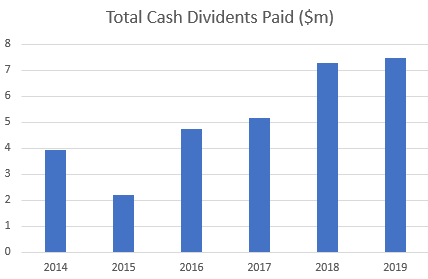
During this time (from IPO) they were also paying dividends:
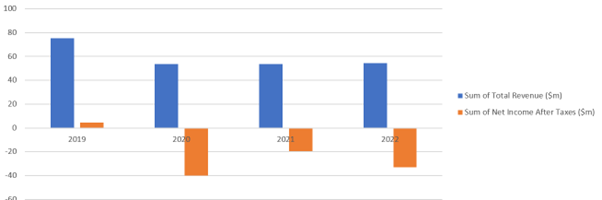
From FY19/20 onwards they have changed their accounting methodology to value their PDPs so that they align with industry practice. (Using Amortised Cost instead of Fair Value). From that point on we have quite a different picture which you can see below. This has been impacted by Carlyle (see below) and the fact that the banks stopped selling them PDP’s when COVID started, so their source of future revenue diminished.
Keith said that PNC pay on average $0.18c on the dollar for the customer accounts that they buy and they seek to earn back 2 ½ to 3 times their investment over a period of 4 – 6 years. Some of it can go on much longer.
The debt classes that they choose to invest in impact the way they evaluate the potential return, the cost for recovery and any reputational risk to their business. Utilities and BNPL may provide a lower recovery rate, so greater emphasis must be put on pricing them correctly. Further, recovery of lower sums may require similar investment in employee time, unless of course they can use technology to create leverage in this space. So when Keith says that the focus is on high quality debt products. This would make sense if they want to reduce their risk of mis-pricing PDPs, steadily grow their team (to be able to liquidate more debt), and create technology assets and better standard operating procedures that can assist them in being able to increase the velocity of debt liquidation without the linear increase in team growth.
Competition
Their major competitor in this space is Credit Corp (ASX:CCP). CCP is the largest debt collection business in Australia. Unlike PNC they have overseas operations in the USA, they are diversified in the types of debt classes they buy, e.g., they purchase BNPL, Utilities and so forth. I still need to research these folks and watch the Strawman Presentation.
It’s interesting to note that it appears that it’s just PNC and CCP buying debt from the major banks now, so the opportunity is there for PNC to take share of wallet from CCP.
Customer Approach
These types of businesses need to be squeaky clean with their customers. Overly bankrupting customers creates reputational risk for the banks selling the debt, so much so that the major banks have previously withheld PDP sales to PNC competitors that are now bankrupt. We saw this borne out by NAB’s decision to cease selling debt to Collection House, who went into administration and was bought out by Credit Corp, (ASX:CCP) in 2022. (https://www.afr.com/companies/financial-services/big-banks-tighten-oversight-of-sales-to-debt-collectors-20190913-p52r00)
To that end, they survey their customers (imagine being asked to fill in a survey when you’re being asked to pay down a debt by a collection agency) and they cite their Net Promoter Score as a key performance indicator, which they deem worthy to report on in their recent investor presentation:
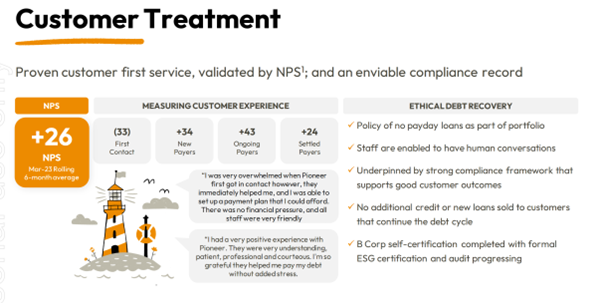
They even state that ‘Vendors preference for Pioneers service differentiation is noticeable’ although I’m not sure they qualify that:

What this missing here is actual NPS numbers; instead, it appears they are citing change to NPS over time, which while helpful, is difficult to understand unless we can also see the nature of business operations during that time.
During the Strawman presentation Keith did speak about how their ethical debt recovery approach drives better outcomes for PNC, their customers as well as the banks. He said by ending debt stress and helping customers to get back on track, they can continue to engage with the banking infrastructure of the country.
Credit Corp (ASX:CCP), their largest competitor, and dominant market player don’t seem to market themselves in quite the same manner.
Were I to invest, one element of the thesis would be that their commitment to provide a positive customer experience is critical to the sustainability of cash flow namely, they can’t afford to be cut off by the banks. If the banks cut them off due to their treatment of customers, they’ll be in trouble, particularly as they don’t appear to be very diversified across debt classes (e.g., BNPL, utilities, etc).
Incentives
There is a focus in both the Good Oil and the Strawman presentations on incentives. This is borne out in the recent annual report.
Whilst the piece around long-term incentives is interesting. Keith John has been issued hundreds of thousands of free shares over the years, and whilst SP on The Good Oil podcast shares his exuberance towards it, the business hasn’t been performing in the last 4 years. Some 8m options were issued to him in 2020 (30c by November 2023), of which 5 million (vested in 2022) had no conditions and the rest are subject to conditions which render them valueless. This was in a year where an acquisition fell through, and there was a $40m loss.
Risks & Issues
They’ve had a rocky couple of years and Keith made a very, very small mention of this in the presentation. A Scheme Implementation Agreement was agreed with Carlyle in Dec 2019, which, had it gone through, would have resulted in Carlyle acquiring all of PNC’s ordinary shares. This also included Carlyle acquiring circa $165m of debt. Shortly after this in 2020, just as COVID-19 was kicking off, Carlyle alleged defaults on the agreement. The agreement was terminated in April 2020 and Carlyle issued a notice declaring that the outstanding amount of $165m was to be paid back to. PNC suggested in a public statement on 14th April 200 that ‘Carlyle are intent on exercising maximum pressure on the Company, including using the potential impacts of COVID-19, to move from their original commitment under the [agreement] and either withdraw from the transaction or attempt to gain control.’ They entered a standstill agreement and subsequently refinanced with Nomura later in 2020, it never went to court, so we’ll never know for sure exactly what happened. At best, a buyer got cold feet and walked away from a deal to buy PNC.
Oh, and then there's that accounting thing.
But all of this is in the past.
Owner Investment
There’s been a significant amount of executive investment in fully paid ordinary shares and options. Just this year alone, in March / April he spent about $165k in shares and $36k in options (2c with strike 80c in Mar 2025). So he’s certainly betting on the company. The extent to which Keith continues to back himself is encouraging
Summary
Whilst PNC is operating in an industry that has a tarnished image, I really like the position that PNC are trying to take in this market. Their focus is on the higher value debt and customer orientated approach, should make them more resilient and protect their sources of assets to liquidate – the banks. Apart from Credit Corp, their competition has largely disappeared through bankruptcy etc. It would be good to see them: be profitable in 2023 per their guidance, start delivering growth of their PDP investments (target of $150m per year) and reduce their cost to recover debt. I will need to do some solid comparative analysis on Credit Corp before I think about making an investment.


 The table above shows the total revenue and employee expenses. I’ve adjusted the CCP employee expenses to use a ratio that discounts based on the proportion of the overall revenue which is attributable to the PDL business (the rest of the revenue comes from consumer lending and other services). This analysis shows:
The table above shows the total revenue and employee expenses. I’ve adjusted the CCP employee expenses to use a ratio that discounts based on the proportion of the overall revenue which is attributable to the PDL business (the rest of the revenue comes from consumer lending and other services). This analysis shows:






